High Molecular Cross-linked Hyaluronic Acid in Osteoarthritis Treatment: An Effective Solution?
Introduction:
Osteoarthritis (OA) is a degenerative joint disease that causes the cartilage in the joints to deteriorate over time. This results in pain, stiffness, and reduced mobility, impacting the quality of life for millions worldwide. Traditional treatments, including pain relief medications, physical therapy, and even surgical intervention, have their limitations. However, a more advanced and promising treatment option is emerging: High Molecular Cross-linked Hyaluronic Acid (HA). This article explores the effectiveness, implementation process, benefits, and potential drawbacks of this therapy in the treatment of osteoarthritis.
What is High Molecular Cross-linked Hyaluronic Acid (HA)?
Hyaluronic acid is a naturally occurring substance in the human body, particularly in the synovial fluid that lubricates the joints. In osteoarthritis, the concentration and quality of this fluid decrease, leading to increased friction in the joint, causing pain and inflammation.
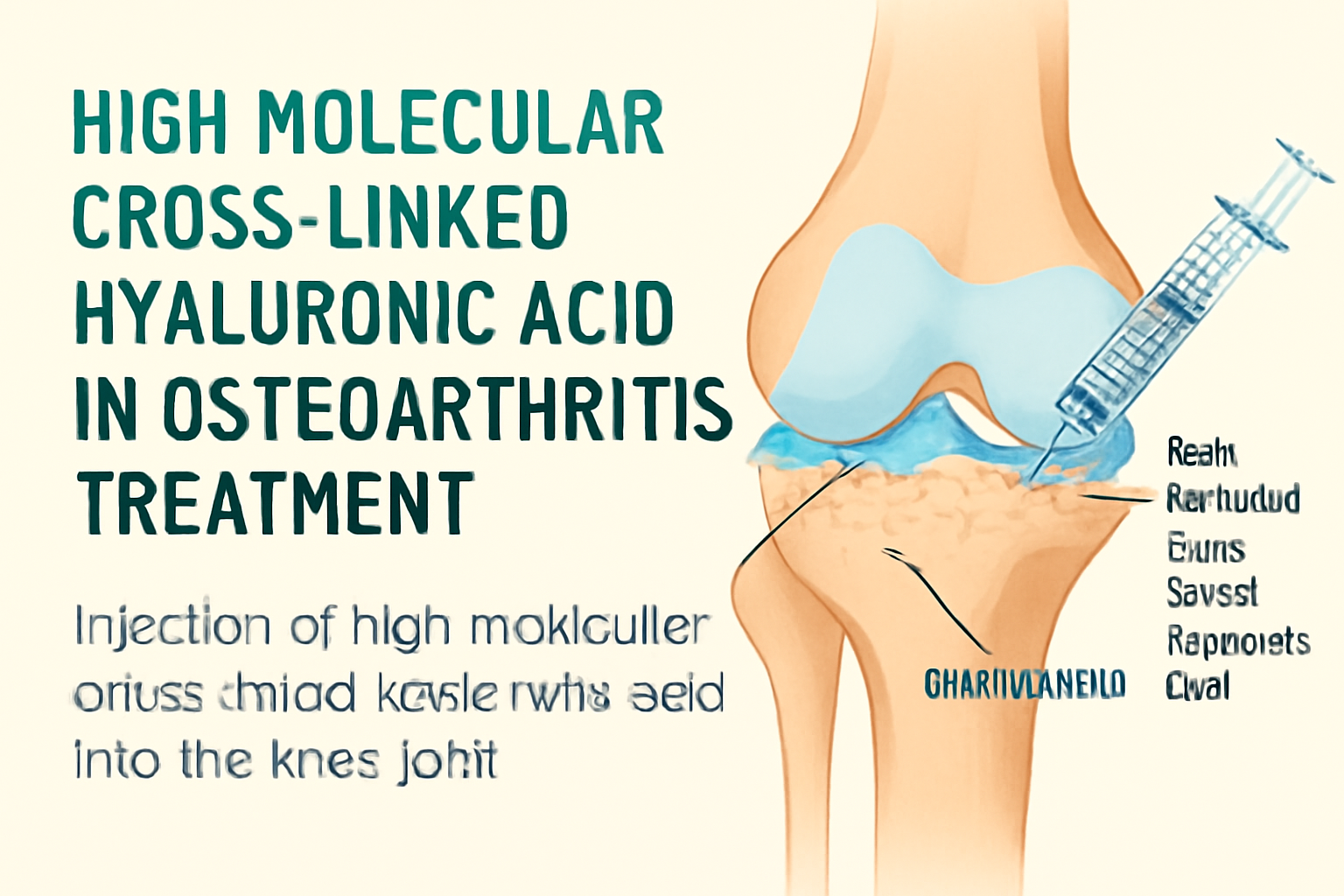
High molecular cross-linked HA is a modified form of hyaluronic acid that undergoes a cross-linking process, which increases its viscosity and stability. This modification improves its effectiveness in providing joint lubrication, enhancing its ability to resist enzymatic degradation and last longer in the joint. When injected into the knee joint (the most commonly affected area), cross-linked HA aims to restore the natural properties of synovial fluid, reducing pain and improving mobility.
The Effective Process of High Molecular Cross-linked HA in OA Treatment
Injection into the Joint:
The process involves injecting a high molecular cross-linked HA solution directly into the affected joint. The procedure typically occurs in an outpatient setting and does not require significant recovery time.
Duration and Frequency:
The number of injections depends on the severity of the condition and the specific product used. Some patients may require a single injection, while others may need a series of three to five injections spaced a week apart.
Mechanism of Action:
Lubrication: The injected HA increases the viscosity of synovial fluid, reducing friction between the bones.
Shock Absorption: The cross-linked HA acts as a cushion, minimizing stress on the cartilage and alleviating pain.
Anti-inflammatory Effect: Some studies suggest that HA injections may reduce inflammation in the joint, further helping to relieve pain and improve function.
Benefits of High Molecular Cross-linked HA in Osteoarthritis Treatment
Pain Relief:
High molecular cross-linked HA provides significant pain relief, often lasting for months after the injection. This can improve overall quality of life and reduce the reliance on pain medications such as NSAIDs.
Improved Joint Mobility:
The restoration of synovial fluid’s natural lubricating properties helps improve joint flexibility and mobility, making it easier for patients to engage in daily activities and exercise.
Minimally Invasive:
The injection procedure is minimally invasive, meaning it doesn't require surgery and has a relatively low risk of complications. It also requires a shorter recovery time compared to other treatment options.
Long-Lasting Effects:
Cross-linked HA tends to last longer than regular hyaluronic acid, providing patients with more durable relief from symptoms.
Alternative to Surgery:
For patients who are not candidates for surgery or want to delay joint replacement, HA injections offer an attractive non-surgical alternative.
Implementation of High Molecular Cross-linked HA in Clinical Practice
In clinical settings, the use of high molecular cross-linked HA has gained popularity as part of a broader strategy to manage osteoarthritis. Typically, patients who are not responding well to nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) or physical therapy may be candidates for HA injections.
It is crucial for healthcare providers to carefully assess the patient’s condition, including the severity of cartilage damage, before recommending HA treatment. Some healthcare professionals combine HA injections with other interventions such as physical therapy, corticosteroid injections, or lifestyle changes to provide comprehensive care.
Conclusion
High molecular cross-linked hyaluronic acid is a promising treatment option for managing osteoarthritis symptoms. It offers patients pain relief, improved mobility, and an alternative to surgery. While the treatment is not without its drawbacks, particularly in terms of cost and temporary effects, it can be an effective solution for many individuals seeking to manage OA without invasive procedures.
As research continues to evolve, it’s likely that new formulations and techniques will improve its effectiveness and accessibility. For patients suffering from osteoarthritis, high molecular cross-linked HA provides a valuable option for improving joint function and quality of life.
References:
Michael R. C., et al. (2020). Hyaluronic Acid Injections in the Treatment of Osteoarthritis: A Review. Journal of Clinical Orthopedics.
Hernandez, C. R., et al. (2019). Cross-linked Hyaluronic Acid for the Treatment of Osteoarthritis: A Review of Recent Clinical Studies. Arthritis Research & Therapy.
Teng, S. M., et al. (2021). Effectiveness of High Molecular Weight Hyaluronic Acid in Osteoarthritis Treatment: A Meta-analysis. International Journal of Rheumatic Diseases.
Published by: Joy Ahmmed
Published on: September 15, 2025
